PRTG comes with a built-in failover cluster for high-availability monitoring. A failover cluster consists of two separate PRTG core server installations, where one server acts as the master node and one server as the failover node.
PRTG includes a single failover cluster with each license, no matter if you use the freeware edition or any commercial edition of PRTG Network Monitor. The cluster feature is not available in PRTG Hosted Monitor.
In this how-to guide, we show you how you can set up a single failover cluster in 6 steps.
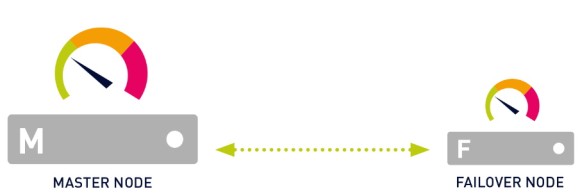
Before you set up your cluster, you need to consider the following requirements:
For more detailed requirements and in-depth information, see the PRTG Manual: Failover Cluster Configuration.
Get full visibility with real-time dashboards, alerts, and customizable sensors
Choose which of your PRTG core servers will act as the master node of the cluster. If you have a PRTG installation that has been running for some time, make this PRTG core server your master node to keep your monitoring configuration.
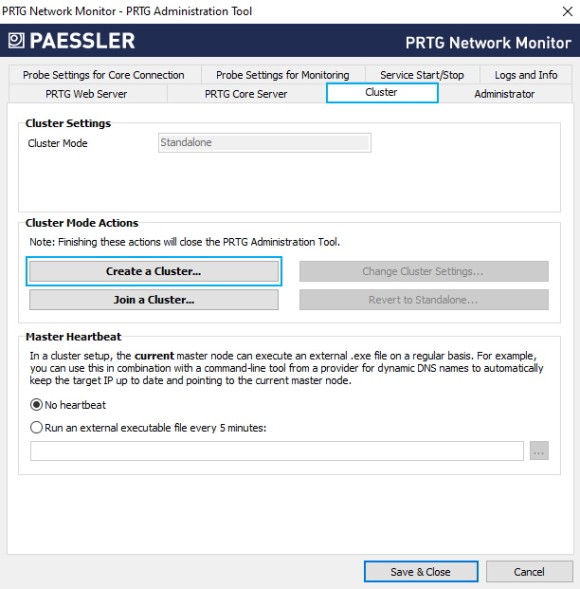
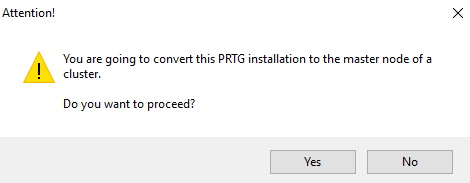
6. Click Create a Cluster and confirm the warning message with Yes.
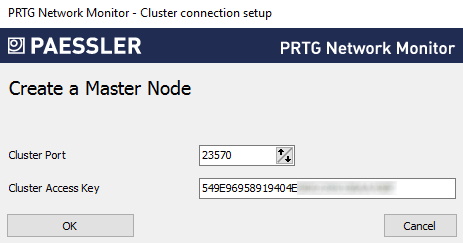
7. Enter a Cluster Port or leave the default value. The port must be open on both the master node and the failover node.
8. Enter a Cluster Access Key or leave the default value. The cluster access key must be unique. Both cluster nodes must use the same cluster access key.
9. Save the cluster access key for later use.
10. Click OK and confirm the message that appears with OK to restart the Windows services and convert the PRTG core server to act as the master node of the cluster.
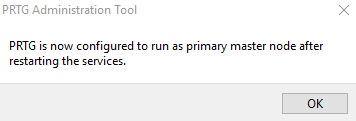
After you have configured the master node, you need to configure the failover node as well.
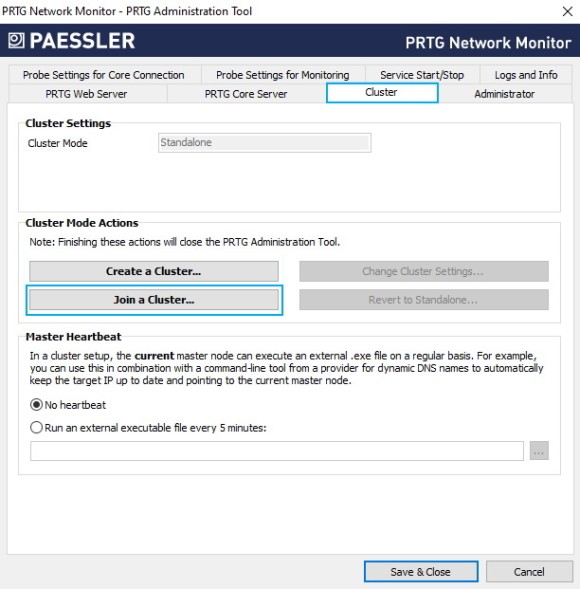
6. Click Join a Cluster and confirm the warning message with Yes.
7. Under Master Node (IP address/DNS name), enter the IP address or DNS name of the master node that you previously configured.
8. Make sure that the Cluster Port matches the port that you previously configured for the master node.
9. Enter or paste the Cluster Access Key that you previously configured for the master node.
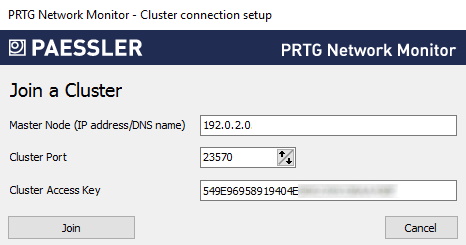
10. Click Join and confirm the message that appears with OK to restart the Windows services and convert the PRTG core server to act as the failover node of the cluster.
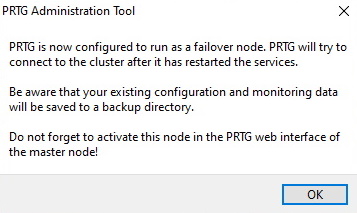
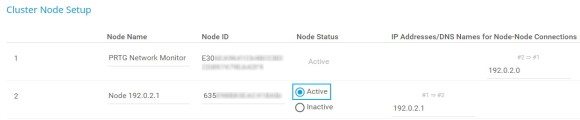
Now that you have configured the master node and the failover node, you need to confirm the failover node by setting it to the Active status in the settings of the master node.
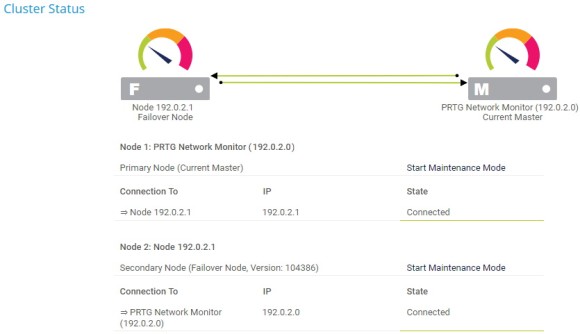
Make sure that the master node and the failover node are connected by checking the cluster status.
If the two cluster nodes have connection issues, check the following log files for any related error messages:
Also make sure that no firewall blocks the connection between the master node and the failover node via the specified cluster port on both sides. If necessary, define NAT rules for your network. See also How to connect PRTG through a firewall in 4 steps.

Custom alerts and data visualization let you quickly identify and prevent all kinds of issues
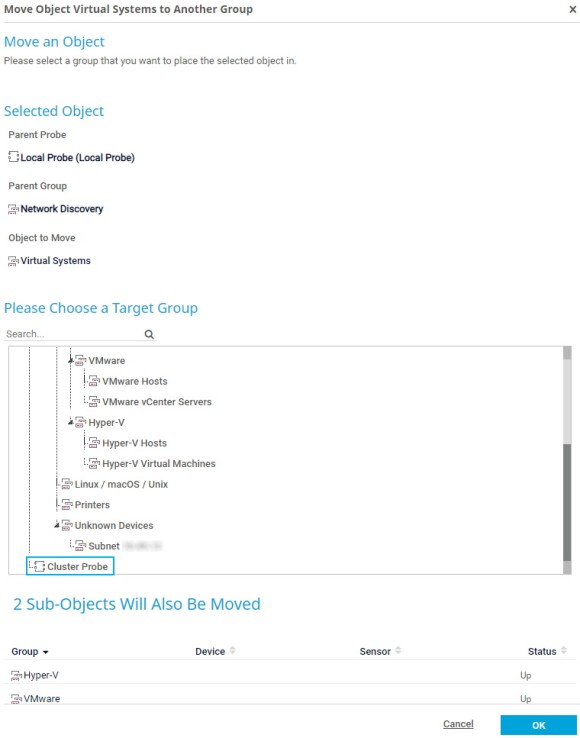
After you set up the failover cluster, you need to move your monitoring objects from the local probe to the cluster probe. This is necessary because PRTG can only monitor objects that are located on the cluster probe via all cluster nodes.
PRTG automatically transfers maps and custom lookup files to the failover node when the master node starts up. However, you need to manually reload custom lookup files on both the master node and the failover node. See also our guide How to work with lookups in PRTG.
In addition, you must manually copy other custom files from the following subfolders of the PRTG program directory on the master node to the respective subfolders of the PRTG program directory on the failover node:
You can add more failover nodes to the cluster at any time. Keep in mind, however, that you need an additional license key if you want to run two or three failover nodes, and two additional license keys if you want to run four failover nodes.
All in all, a failover cluster can consist of a maximum of 5 cluster nodes: one master node and up to four failover nodes.
Also keep in mind the performance considerations mentioned at the beginning of this how-to guide.